TRAIDA
AI & Data solutions
In this sphere, you will find best practices for building your technical architecture to scale AI. You will need to clarify your data management systems, likely using knowledge graph technology, and possibly a NoCode or LowCode database depending on the complexity of your business. To analyze needs and conduct a phased transformation, we have defined the TRAIDA framework (Transformative AI and Data Solutions) which contains essential knowledge both technically and in terms of governance.
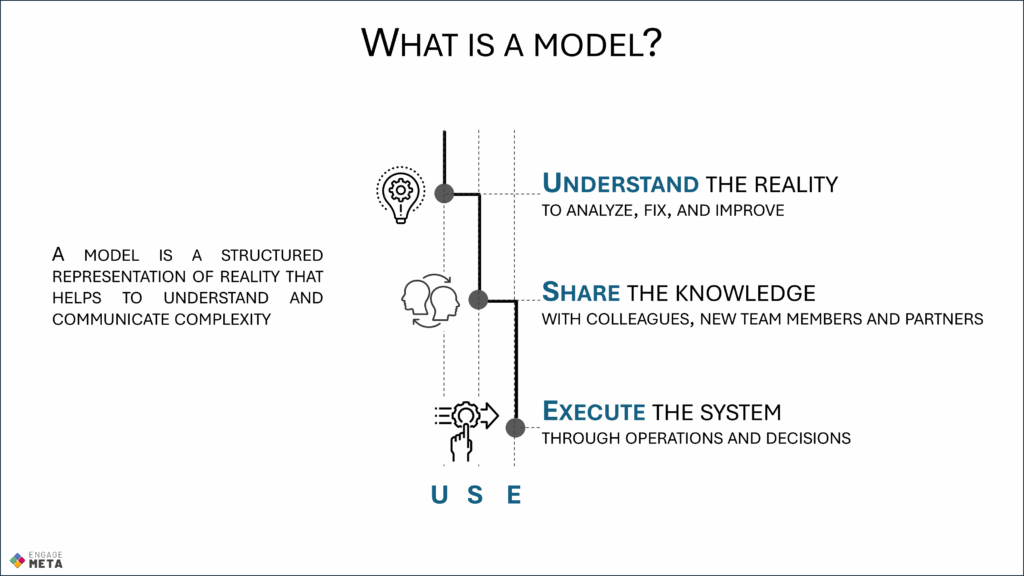
Why We Need Models?
Fast-Track Training: Why We Need Models: Strengthening Data Governance for AI
This deck explains why models are essential tools to understand, communicate, and govern complexity in the age of AI. It shows how models drive operational efficiency, support data governance, and provide the foundations for trustworthy AI and knowledge management. From Occam’s razor to the data management organization, the slides highlight best practices for building models that are simple, extensible, and usable in daily decision-making.
Download the training deck HERE.
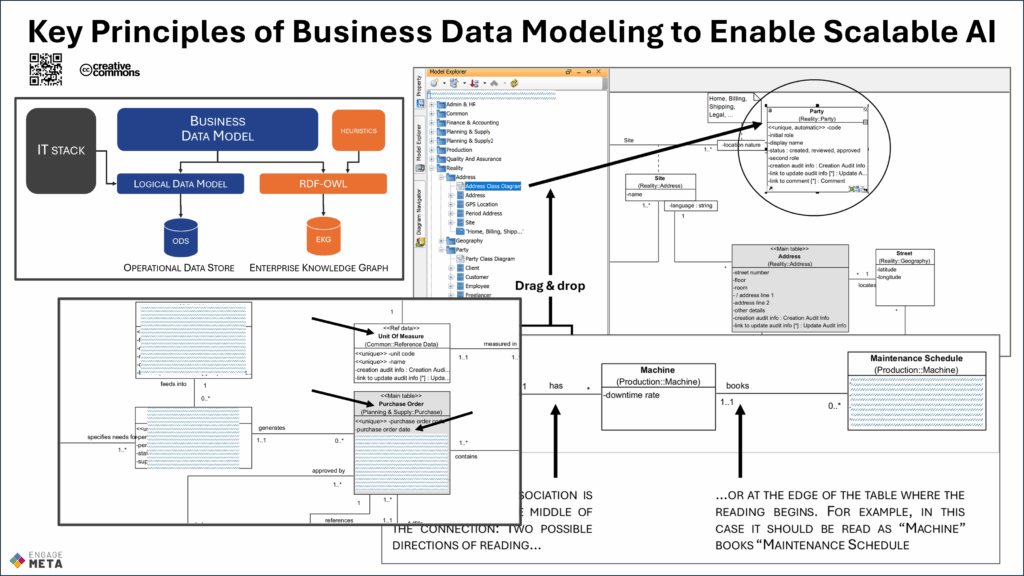
Business Data Modeling to Enable Scalable AI
Fast-Track Training: Key Principles of Business Data Modeling to Enable Scalable AI
This training introduces the key principles of business data modeling and explains why it is the cornerstone for deploying Artificial Intelligence at scale. By structuring data around business concepts, organizations can move beyond fragmented spreadsheets and inconsistent definitions, building a solid foundation for enterprise knowledge graphs, advanced analytics, and AI-driven automation.
Download the training deck HERE.
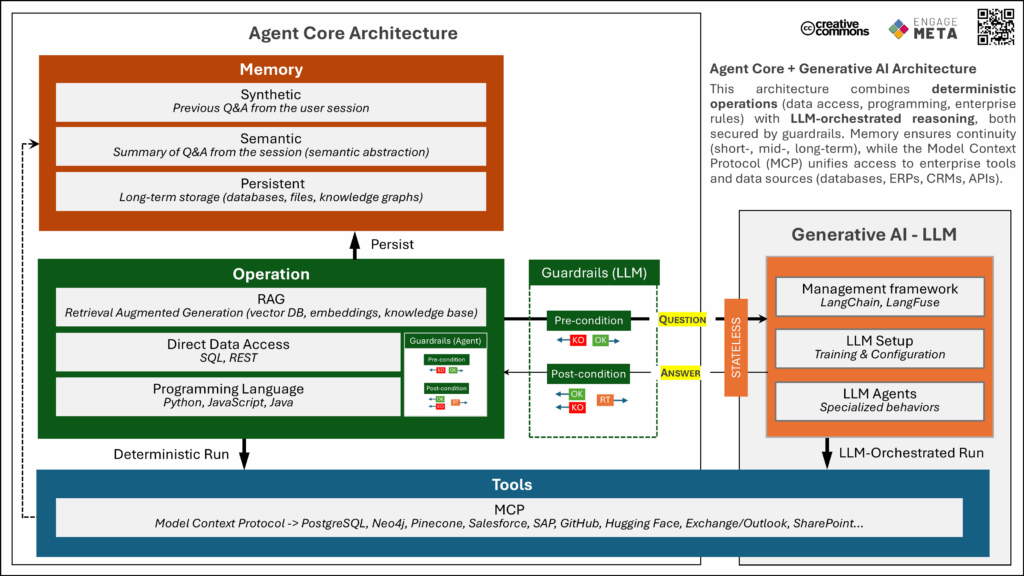
Agent Core + Generative AI Architecture
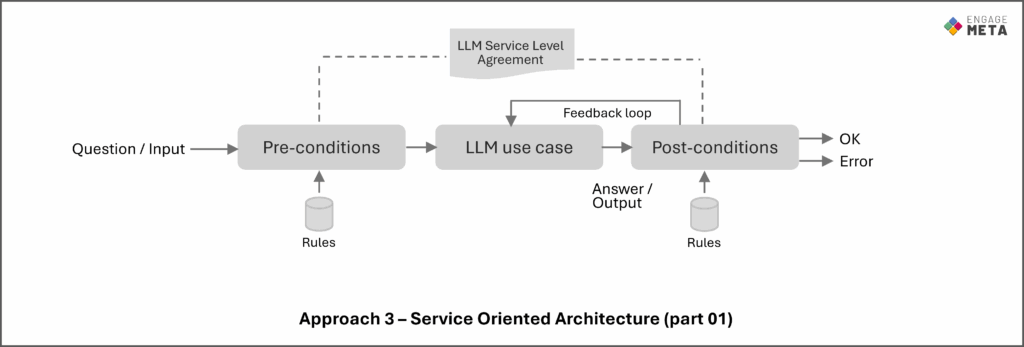
Here is our latest Agent Core + Generative AI architecture framework.
It shows how deterministic operations, LLM-orchestrated reasoning, guardrails, and the Model Context Protocol (MCP) come together to ensure continuity, governance, and interoperability across enterprise tools and data sources.
A step forward in building trustworthy, scalable AI agents.
Because LLMs exhibit non-deterministic behavior, their execution must be constrained by pre- and post-conditions, in line with the classical Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) pattern.
Download our study on combining LLMs and SOA HERE.
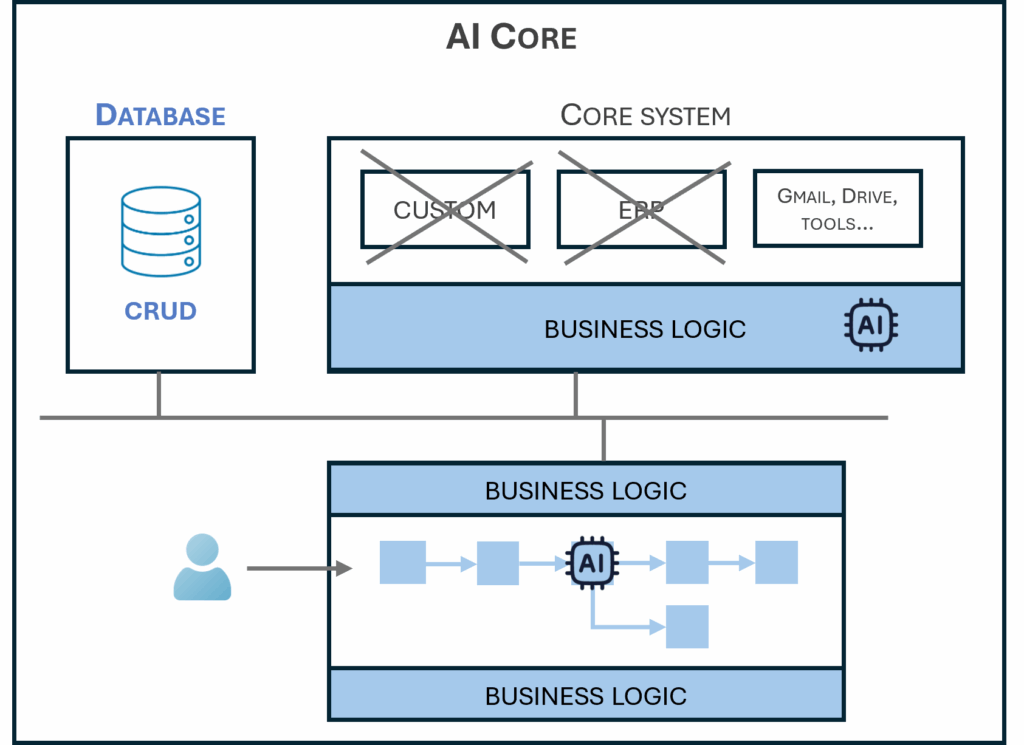
IT Stack - AI-NoCode-Data
The technical architecture is based on a series of software components that form a stack, including data management, automation tools (workflows), and AI solutions.
Each software component is integrated into a global execution platform, which can be either managed on the company’s premises (on-premise) or hosted by a provider (SaaS, Cloud). Given the level of technical expertise required to ensure the security and scalability of both the software and the execution platform, it is recommended to delegate their installation and administration to a specialized service provider. Therefore, the choice of technical scenario must also consider selecting an IT service provider capable of operating the chosen software stack.
The choice of technical scenario must be compatible with the selected provider for operating your IT systems. It is crucial to ensure that the provider is capable of installing and managing the chosen technologies while meeting the expected performance, security, and cost requirements.
Choosing your IT stack for AI, NoCode, and Data is like choosing a vehicle for a journey.
You start at point A, and you want to reach point B—but you may eventually head to C or D. Some people need speed, others need space for family, pets, or business cargo. Your choice depends on your goals, budget, ethics (fuel vs. electric), and future plans. Just like a sports car, van, or electric SUV, your tech stack must fit your specific needs. Do you need fast prototypes or long-term scalability? Manual control or automation? The road you choose—flat highways or winding trails—also impacts your decision. A bad fit means higher costs, delays, and inefficiencies along the journey.
The right stack, like the right car, gets you there smoothly, with room to adapt. That’s why an architecture study is essential: it helps you pick the right “vehicle” now.
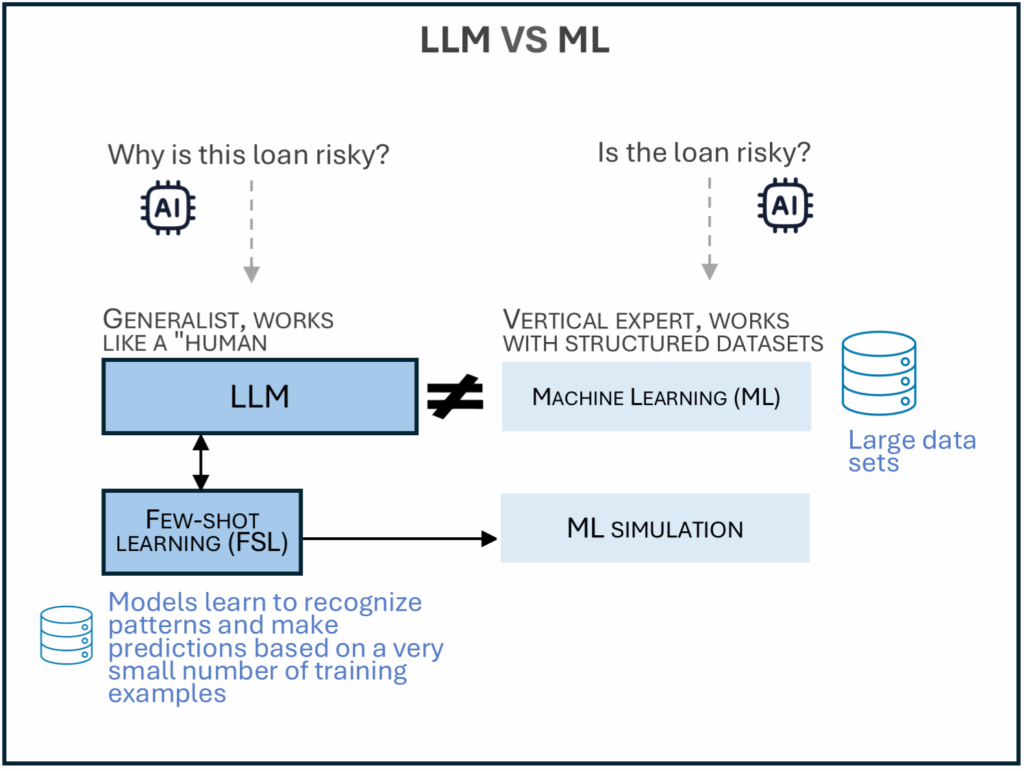
Traditional ML models require task-specific training with large labeled datasets. LLMs are pretrained on massive text corpora and can generalize across many tasks.
Few-shot prompting lets LLMs perform tasks by showing just a few examples in the prompt. This mimics supervised ML without the need for model retraining or fine-tuning.
ML models need to be retrained when the task changes; LLMs just need a new prompt. Few-shot LLMs are flexible but may be less accurate than fully trained ML models.
LLMs can handle structured and unstructured data directly from natural language.
ML often requires feature engineering, while LLMs use text as-is. LLMs are ideal for prototyping or when labeled data is scarce. Few-shot learning shows how LLMs can act like ML models—without training a new one.
AI Financial Assessment Framework
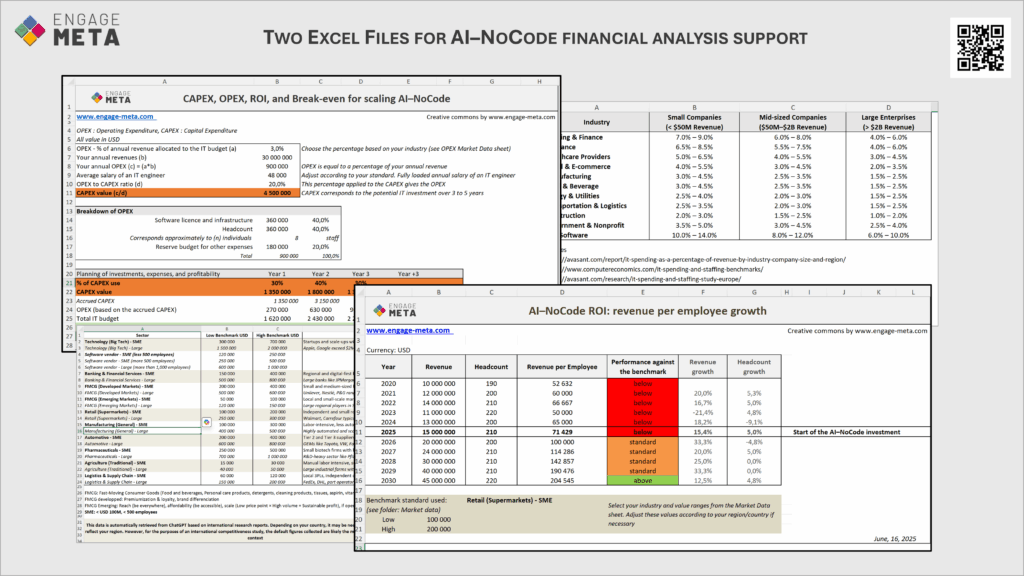
We believe it’s essential to clarify the values of CAPEX and OPEX for the company’s IT system by comparing them with market standards. Then, we recommend analyzing the expected productivity gains from AI by measuring them based on the average revenue generated per employee over the years.
To compute your CAPEX, OPEX, ROI (and break-even), download the two Excel sheets made freely available to you by the Engage-Meta community. They are simple and effective.
Aiming to scale AI across the company without clarifying CAPEX, OPEX, ROI (and break-even) leads to a chaotic process. On the other hand, trying to precisely calculate the costs and expected benefits of AI over several years in a reliable way is nearly impossible—everything changes too quickly, both technically (e.g., token pricing) and in terms of ideas that reshape how we work.
What remains stable, however, are your CAPEX, OPEX, and the key indicator of average revenue generated per employee over the years. These financial values provide a solid foundation for building a 3- to 5-year roadmap—strong enough to engage decision-makers and all company stakeholders.
Of course, CAPEX should support a deep overhaul of the existing IT system to eliminate silos and integrate AI at scale under the best conditions—effectively a kind of rebirth for corporate IT. Without strong, market-standard CAPEX, large-scale AI deployment simply isn’t possible.
Download the CAPEX-OPEX Excel file HERE.
Download the ROI (Revenue per employee) Excel file HERE.
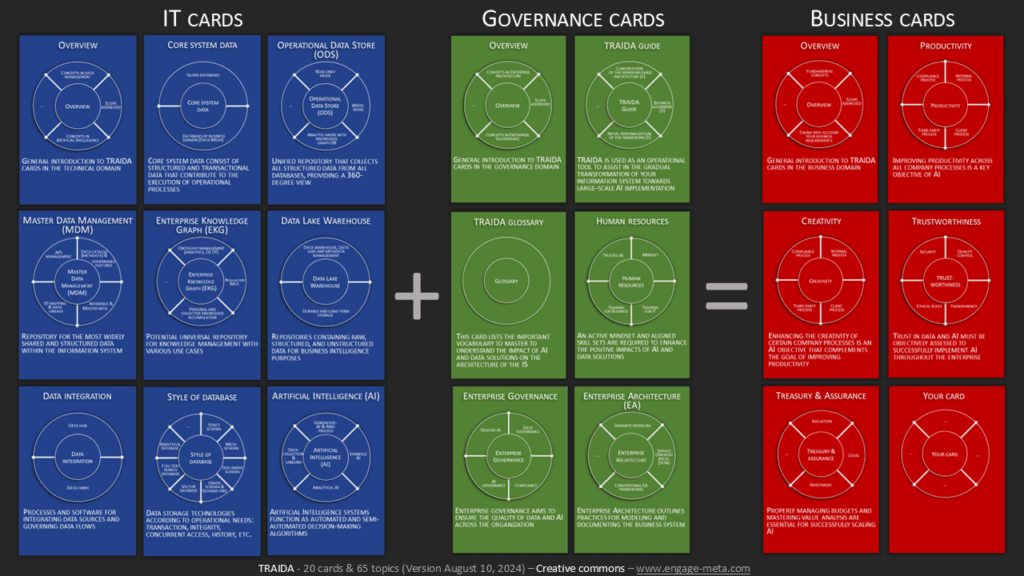
The TRAIDA cards
Click HERE or on the image to download the PDF of the global map. The TRAIDA framework consists of 20 cards and 65 topics to address AI and the associated data solutions. Here you will find 9 technical cards (30 topics), 6 governance cards (17 topics) and 5+ business cards (18 topics). Each TRAIDA card is accompanied by a concise documentation that explains its importance in improving data quality and the use of AI on a large scale within the company. With its 20 cards and 65 topics, it offers a comprehensive view of enterprise architecture approached through the lens of data management and AI.
Here is the introductory slide deck for the TRAIDA cards. You can freely use it in your projects, courses, and commercial offers. By doing so, you contribute to the alignment of IT and Business for AI, thanks to the blue, red, and green cards!
Download HERE (PDF) (last update: November 04, 2024)
TRAIDA relies on a semantic platform architecture
Click HERE or on the image to download the PDF of the semantic platform architecture.
TRAIDA is based on an architectural vision that places a semantic platform at the center of the business system, essential for complete data quality control and scaling up AI.
TRAIDA white paper
Reconciling expertise in data governance, Enterprise Architecture (EA), and Artificial Intelligence represents a considerable challenge. This is the theme of our white paper, which proposes a comprehensive approach for the large-scale deployment of AI in companies.
The slides from the TRAIDA Masterclass presentation are available for free download HERE (+200 slides). Feel free to contact us if you need to organize this masterclass at your company. Thank you!
Last update: August 17, 2025
You can download the deck of this video here (PDF).
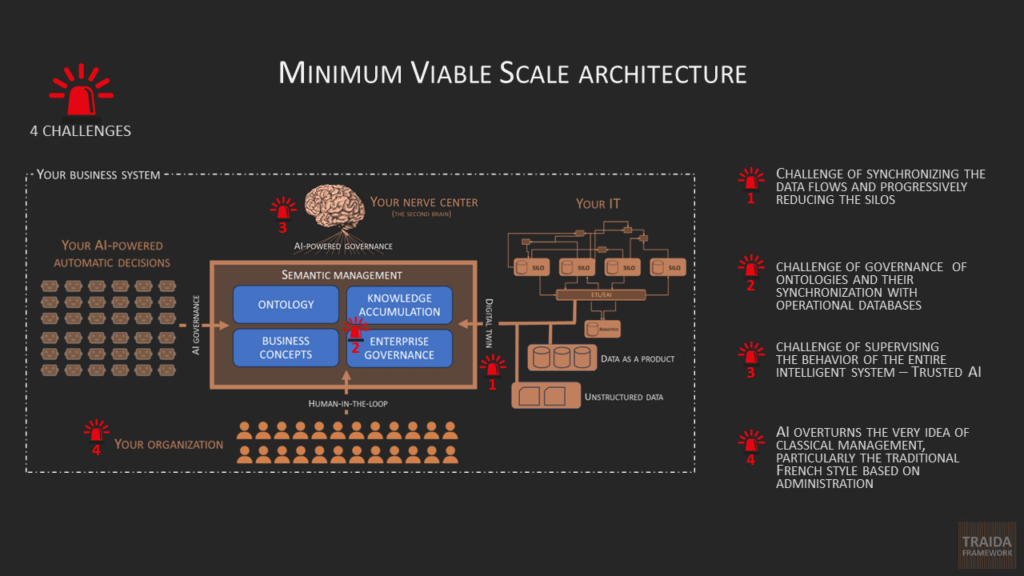
MAINTAIN CONTROL OF YOUR IT + AI THROUGH THE MINIMUM VIABLE SCALE (MVS) ARCHITECTURE
Rather than forcing the definition of technical and business EA targets, the company first compares itself to a set of essential topics for large-scale deployment of AI and associated data solutions.
The goal is not to try to describe targets on a wide range of topics, but to limit the analysis to AI and data management. We start from the principle that the minimally viable technical architecture is based on these two devices: AI and data management.
It is important to emphasize the significance of this concept of “minimally viable architecture”, also qualified as “Minimum Viable Scale – MVS”, which aptly illustrates the idea of progressively scaling the architecture.
Download the executive summary (PDF): In ENGLISH and FRENCH.
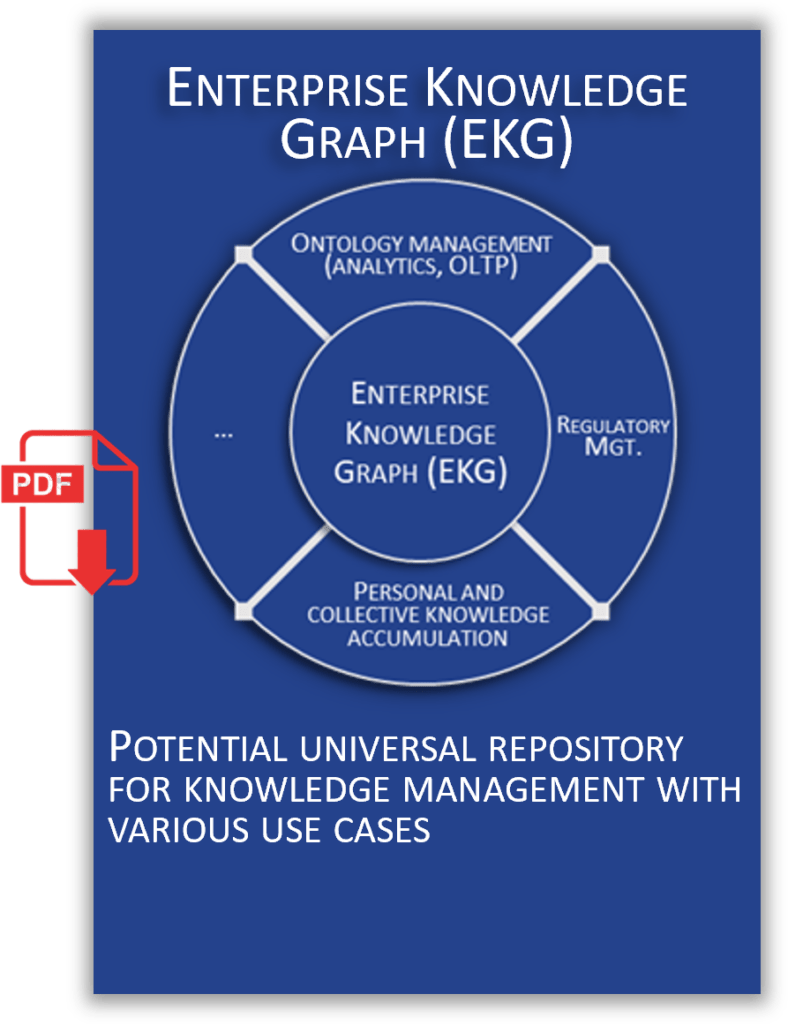
Transformative AI and data solutions demand a robust semantic management layer for scalable deployment. Within this slide deck, we aim to demonstrate the operation of such integration, elucidating key concepts including the digital twin, human-in-the-loop, AI governance, AI-powered governance (often dubbed the ‘second brain’), and semantic management. Unsurprisingly, at the core of this architecture lies a knowledge graph repository, essential for managing ontologies and facilitating the accrual of knowledge.
Vision (#1)
Slide deck with 61 slides, creative commons license, open-source, PDF 5,529Kb
- The context of our approach
- A vision for transformative AI and data solutions
- Alignment of our vision with the market
- The TRAIDA framework
- The final report deliverable
- Evaluation process
AI impacts (#2)
Slide deck with 104 slides, creative commons license, open-source, PDF 8,482Kb
- Impacts on the business
- Impacts on the IT system
- Integration with Enterprise Governance (EG)
- Integration with Enterprise Architecture (EA)
- Post-consultation services
- AI software list
As a seasoned Data Management expert with an extensive background in non-schema oriented databases and semantic modeling, I view the knowledge graph repository as a contemporary reimagining of the traditional MDM concept—more versatile and semantically aligned with the business systems of any organization. It goes beyond the traditional scope of merely handling master and reference data, encompassing a wide array of data types, processes, and critical rules.
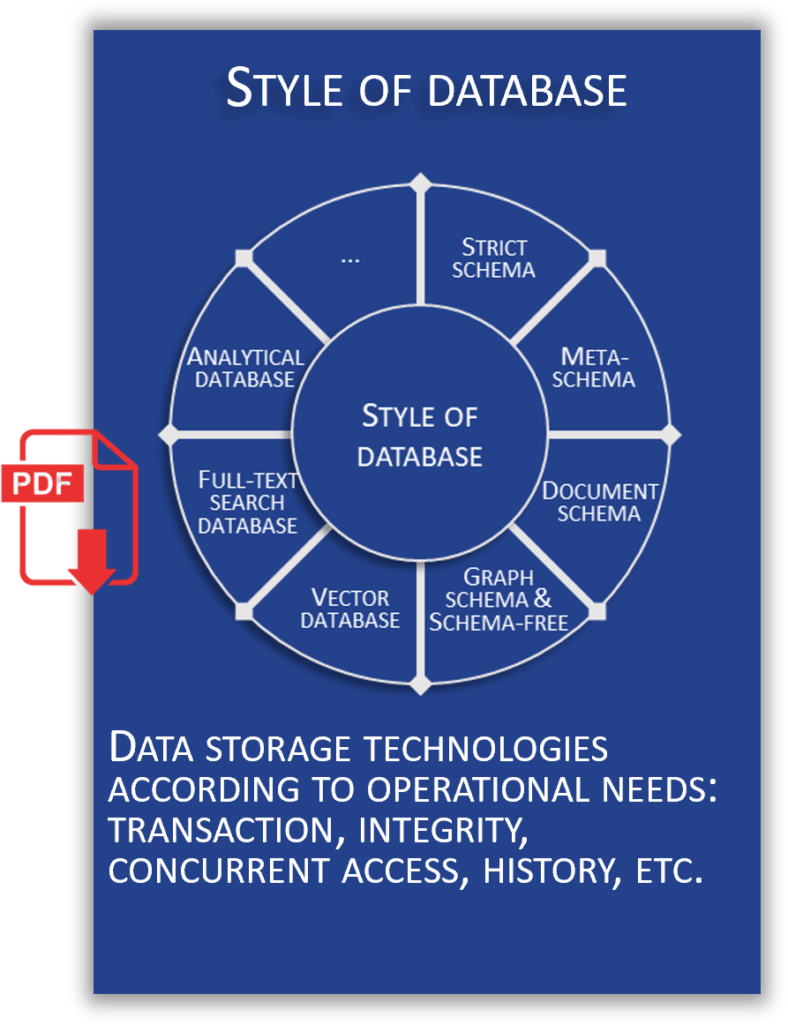
Watch this video to find out more about the various database schema styles: strict-schema, meta-schema, dynamic schema, schema-less or document-schema, graph schema, and schema by convention.